Flame retardant (FR) additives are commonly used to improve fire-safety of synthetic polymers, which are widely employed in manufactured consumer goods. The incorporation of a FR in a polymer typically leads to deterioration of its mechanical properties. It also manifests itself in a non-negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs) release, which in turn increases environmental risks carried by both the application and disposal of the corresponding consumer goods. We presented a hierarchical strategy for the design of composite materials, which ensures simultaneous improvement of both mechanical and fire-safety properties of polymers while limiting the VOC release. Our strategy employs porous metal organic framework (MOF) particles to provide a multifunctional interface between
the FR molecules and the polymer. Specifically, we demonstrated that the particles of environmentally friendly HKUST-1 MOF can be infused by a modern FR – dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP), and then embedded into widely used unsaturated polyester. The DMMP-HKUST-1 additive endows the resulting composite material with improved processability, flame retardancy and mechanical properties.
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis and computational modeling of the additive suggests the complete pore filling of HKUST-1 with DMMP molecules being bound to the open metal sites of the MOF.
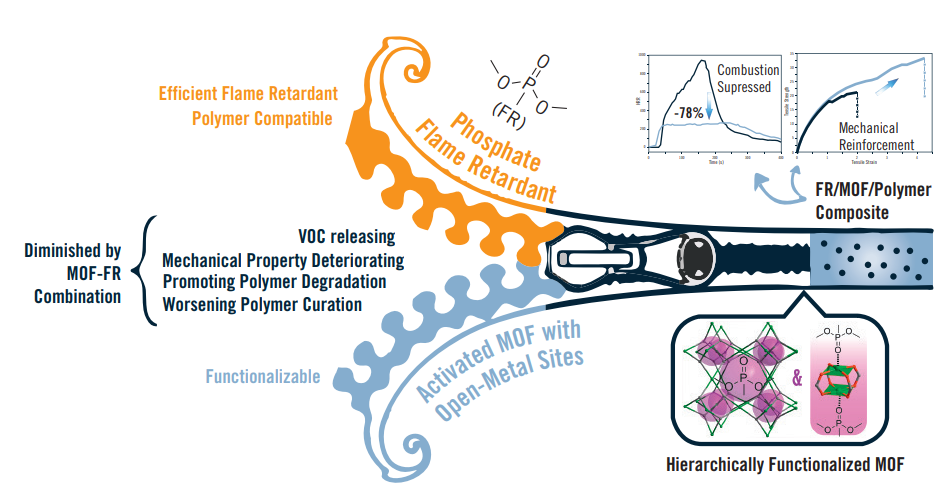
Schematic depiction of merging properties of a polymer and a flame retardant-filled MOF particles.
Simultaneous Improvement of Mechanical and Fire-Safety Properties of Polymer Composites with Phosphonate-Loaded MOF Additives
X.-L. Qi, Dong-Dong Zhou, J. Zhang, S. Hu, M. Haranczyk* and D.-Y. Wang*.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 22, 20325-20332, 2019.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b02357
